Molecules:
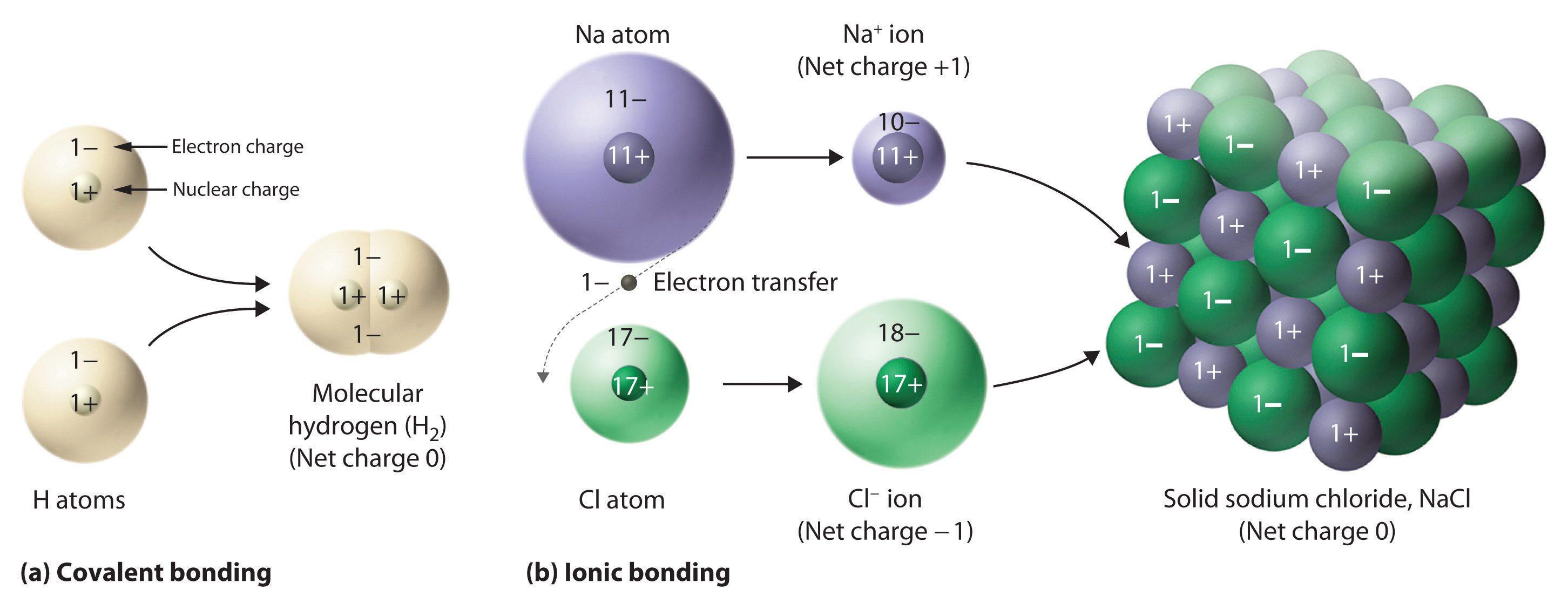
Atoms can join to form larger things called "Molecules" just like you can join pieces of a puzzle to make larger individual pieces or you can join LEGOs to build larger things. The things around us are all actually structures formed by trillions and trillions of molecules, ion pairs, metal atoms or a mixture of these things (depending on what type of thing it is). If you are wondering how atoms bond (join together), click here.
Definition:
"A molecule is the smallest particle in a chemical element or compound that has the chemical properties of that element or compound."
OR
"A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction."
Simplified
When two or more atoms bond (stick together), a "molecule" is said to be formed. The joining together of atoms is discussed in the post: Duplet, Octet, Valency and Chemical Combination/Bond. Atoms by the use of electrons join each other and become independent molecules, these molecules together form all other things like us and the objects around us. The properties of elements are lost and new properties are achieved like sometimes the color changes, it becomes harder etc. It is the smallest particle of a compound which can exist independently and shows all properties of a compound. Molecules are neutral and stable.
Types:
There are many types of molecules:
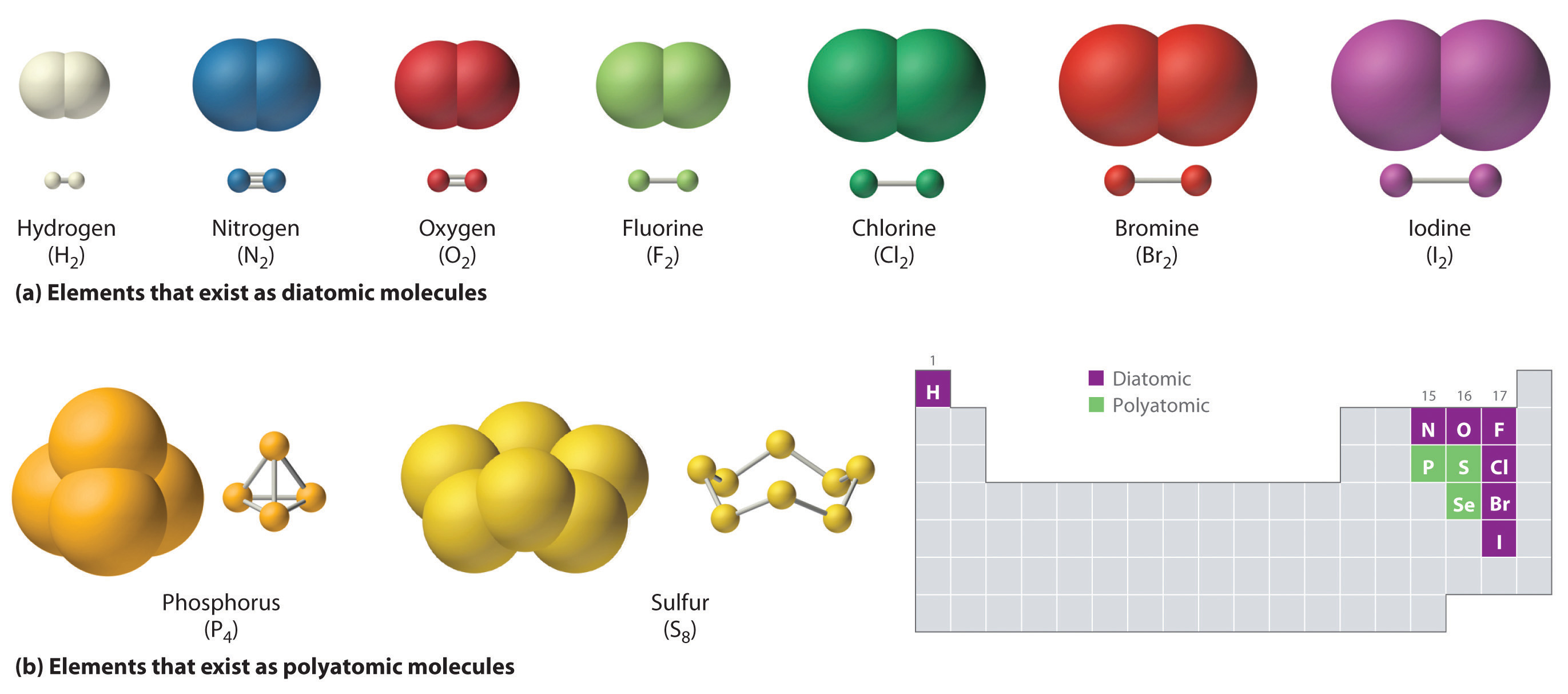
Di-Atomic & Tri-Atomic Molecules:
A molecule made up of 2 atoms bonded together is called a "Di-atomic Molecule", 3 atoms bonded together: Tri-atomic Molecule" and so on. e.g. tetra atomic (4 atoms), penta-atomic (5 atoms), hexa-atomic (6 atoms).
Poly-Atomic Molecules:
Poly-Atomic Molecules:
A molecule made up of 2 or more atoms bonded together is called a "Poly-Atomic Molecule". Di-atomic & tri-atomic molecules can also be called poly-atomic molecules.
Homo-Atomic Molecules:
A molecule made up of the same types of atoms is called a "Homo-Atomic Molecule" e.g. if 2 hydrogen atoms bond, a homo-atomic molecule is formed. It is called homo-atomic because the same type of atoms form it (hydrogen).
Hetero-Atomic Molecules:
A molecule made up of different types of atoms is called a "Hetero-Atomic Molecule" e.g. if flourine and hydrogen stick together, a hetero-atomic molecule is formed because they are 2 different atoms.
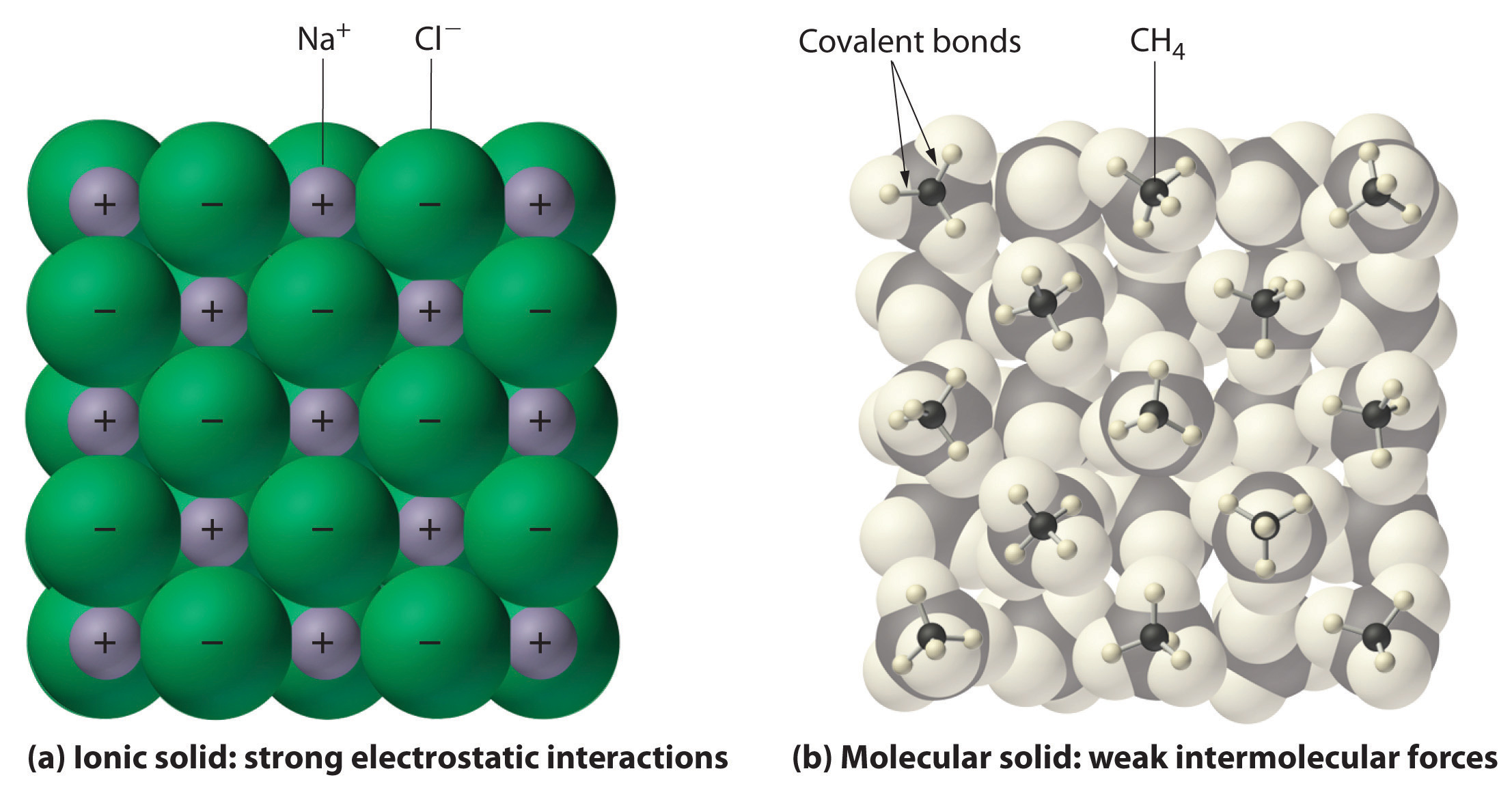
Compounds:
A compound is formed by the chemical combination (bonding/sticking together) of atoms of different elements in a fixed ratio by mass. For example: Carbon Dioxide is formed when 2 oxygen atoms and 1 carbon atom stick together. It's ratio by mass is 12:32 (as the mass of carbon is 12 and of 2 oxygen atoms is 16 plus 16 = 32.) It can be simplified: 12:32 = 3:8
In chemistry, breaking down means "breaking the bonds and thus making it smaller and simpler" like you can separate the the pieces in a puzzle. Compounds cannot be broken down (changed back to the elements that joined to form them) by simple ways, it is a bit difficult. For example, the compound water (H2O) can't be broken down to hydrogen and Oxygen gases by simple methods.
Properties:
Elements have specific properties like their own hardness, color and smell etc. When they join to form a compound, these properties change. Now, the compound formed by the combination of those elements has a different color, smell, taste, melting & boiling point etc.In chemistry, breaking down means "breaking the bonds and thus making it smaller and simpler" like you can separate the the pieces in a puzzle. Compounds cannot be broken down (changed back to the elements that joined to form them) by simple ways, it is a bit difficult. For example, the compound water (H2O) can't be broken down to hydrogen and Oxygen gases by simple methods.
Types:
There are 4 main types of compounds:
1.) Covalent compounds (Polar and Nonpolar), Ionic compounds, Metallic Compounds and Coordinate Covalent Compounds. They shall be discussed later.
1.) Covalent compounds (Polar and Nonpolar), Ionic compounds, Metallic Compounds and Coordinate Covalent Compounds. They shall be discussed later.
 |
| Water / H2O, a tri-atomic molecule with 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom. (The fourth atom is a part of another water molecule.) |
 |
| Carbon Dioxide |
No comments:
Post a Comment